-
iestinstrument
High-Precision Electrochemical Workstation Testing Equipment: A Critical Enabler for Breakthroughs in Electrochemical & Energy Storage
1. Preface
In the field of electrochemistry, electrochemical workstation testing equipment is a key tool for researching and developing new battery technologies. With the rapid advancement of new energy technologies, high-precision electrochemical workstation testing equipment has become increasingly important in battery evaluation. Charge and discharge equipment is primarily used to assess the consistency, safety, functionality, and reliability of lithium batteries, making it an indispensable component in the production, R&D, and application stages of lithium batteries.
2. Policy Context and Industry Shift
On May 8 of this year, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology solicited opinions on the standardized conditions and announcement management measures for the lithium battery industry, aiming to guide companies away from projects that merely expand production capacity, and to emphasize technological innovation and product quality improvement. The market has shifted competition in the battery industry from a focus on quantity to one driven by quality. As a critical product in the new energy sector, how can charge and discharge equipment help the battery industry achieve a qualitative leap and effectively support its healthy development?
3. Why Must Charge and Discharge Equipment Be Highly Precise?
During battery development and optimization, the accuracy of test data directly determines the reliability of research outcomes. High-precision battery charge and discharge equipment delivers precise electrochemical parameters, enabling researchers to probe subtle physical and chemical transformations within batteries. These micro-scale phenomena can only be resolved with instrumentation of exceptional resolution.
3.1 Precise Current and Voltage Measurements
In the charge and discharge process, variations in current and voltage are fundamental parameters that characterize battery performance. High-precision measurements not only ensure the authenticity of the data but also help identify potential performance issues; even minor voltage fluctuations may signal battery degradation. Currently, mass-produced devices typically offer accuracies of 0.1% or 0.05%, primarily used for cycle testing and verification of battery cells. For charge and discharge equipment, voltage and current precision involve two aspects: control precision and measurement precision. Although related, these have distinct meanings and improvement methods.
In simple terms, a device is a stack of components controlled by specific logic to perform desired functions. Selecting high-quality components not only enhances the device’s precision but also ensures long-term stability. High-precision and stable charge and discharge equipment requires substantial investment during the component selection phase, which is why ultra-high precision charge and discharge (UHPC) systems can cost dozens of times more than standard equipment.
3.2 Control Precision
Control precision refers to the device’s ability to accurately adjust and maintain the target voltage or current. This determines whether the equipment can operate at the set values during charge–discharge cycles without deviation. The key factor here is the hardware’s control capability, achieved through high-precision digital signal processors (DSPs) or microcontrollers that enable precise control of voltage and current. The hardware design involves multiple aspects, such as the design of precision power supplies and control circuits, which can effectively reduce noise and interference, ensuring that the device responds quickly and maintains stable setpoints. Additionally, the use of low-temperature-drift and low-time-drift resistors, precision capacitors, and other high-quality components can minimize errors due to temperature variations and aging—commonly referred to by R&D personnel as “temperature drift and time drift.”
3.3 Measurement Precision
Measurement precision is the ability of the device to measure the actual voltage or current close to its true value, reflecting the accuracy and stability of the measurement system. The key component here is the device’s measurement system, i.e., the data that users read on the control software. Essentially, the hardware converts the analog signal to a digital signal via a high-precision analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and then transmits it to the software for user access. Achieving high testing accuracy requires optimizing the measurement circuit to reduce noise and errors introduced during the measurement process. For instance, employing a four-wire measurement method can eliminate the influence of lead resistance. Furthermore, users should periodically calibrate the device channels, which serves as both a verification and an adjustment for measurement precision affected by hardware time drift and temperature drift.
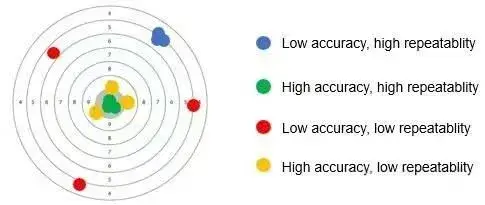
Figure 1. Accuracy and Repeatability Target Chart
3.3.1 Accuracy vs. Repeatability: A Dual Paradigm
In practical applications, both control and measurement accuracies are critical. Control accuracy ensures precise execution of test protocols, while measurement accuracy guarantees reliable feedback for adaptive control and data analysis.
3.3.2 Deciphering Manufacturer Specifications
Equipment datasheets often conflate accuracy metrics under a single parameter, typically denoting test accuracy—the user-observable metric reflecting end-to-end system performance.
IEST Instrument, as a professional supplier of lithium battery testing equipment, has developed its products over many years by addressing diverse customer needs and pain points. The high-precision charge and discharge equipment products are designed to meet increasingly stringent standards and offer customized services. The current development equipment features eight test channels with an accuracy of 0.01%, integrating electrochemical workstation such as CV (cyclic voltammetry) and EIS (electrochemical impedance spectroscopy). These enable seamless integration of CV/EIS steps into long-term cycling protocols, empowering users to monitor dynamic electrochemical properties during aging studies.
Figure 2. IEST Electrochemical Property Analyzer Series
| ERT6008 VS ERT7008 | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|
| Name | ERT6008: High Precision CV Test System | ERT7008: High Precision CV+EIS Test System |
| Accuracy | ±0.01% F.S. | ±0.01% F.S. |
| Voltage | ±5V | ±5V |
| Current Range | 1:100mA 2:12A |
1:100mA 2:12A |
|
Electrochemical |
CV/LSV/PITT/GITT/CA/CP |
EIS/CV/LSV/PITT/GITT/CA/CP |
| EIS Testing | × | 0.01Hz~100kHz |
4. Application Landscape
While user-specific applications vary widely, high-precision charge-discharge systems ultimately address three core challenges:
4.1 Energy Density Optimization
By precisely quantifying capacity, voltage plateaus, and cycle life of novel materials, researchers identify pathways to higher energy densities, accelerating the development of more efficient and durable batteries.
4.2 Safety Enhancement
High-resolution systems detect latent failure modes—overcharge, overdischarge, thermal runaway—enabling design improvements to mitigate risks.
4.3 Lifetime Extension
Multi-parameter aging analysis (e.g., long-term cycling coupled with impedance tracking) unravels complex degradation mechanisms, informing strategies to prolong battery service life.
For expanded discussions on these applications, refer to our technical article: “The Significance of High-Precision Charge/Discharge Testing for Predicting the Lithium ion Battery Lifespan” (available on our official platform).
5. Conclusion
As practitioners in instrumentation R&D, we recognize the pivotal role of technological innovation in data accuracy. While the progressive localization of precision equipment reflects industry advancement, ensuring long-term measurement stability remains a systemic challenge.
The intense competition within China’s new energy sector has, on one hand, enabled technological leapfrogging and global leadership. However, sustaining this leadership demands relentless innovation—surpassing competitors is not the endgame; perpetual self-improvement is.
Contact Us
If you are interested in our products and want to know more details, please leave a message here, we will reply you as soon as we can.